The Essentials of Circulating Supply in Crypto
With the growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) and the cryptocurrency market in general, it is no wonder that an increasing number of users want to learn what it takes to trade crypto as safely as possible. Whether we’re talking about a $100 or a $1 million investment, your funds should always be safe, and your trading and […]

With the growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) and the cryptocurrency market in general, it is no wonder that an increasing number of users want to learn what it takes to trade crypto as safely as possible. Whether we’re talking about a $100 or a $1 million investment, your funds should always be safe, and your trading and investing techniques should be up to date. Unlike fiat currencies, where things are a bit different, in crypto, you can leverage specific metrics, including the circulating supply.
This article will provide information about the circulating supply, focusing on what it is and its impact on various concepts in the cryptocurrency industry.
What Is Circulating Supply?
The circulating supply refers to the number of cryptocurrency coins or tokens available for public trading at a given time. Unlike the total supply, which includes coins held in reserve or not yet in circulation, the circulating supply focuses only on those coins that can be actively bought or sold on exchanges.
For instance, Bitcoin’s circulating supply refers to the number of bitcoins available on exchanges or held by individuals, excluding those that have yet to be mined. By observing the circulating supply, investors gain a clearer understanding of a coin’s availability in the market and how this may impact its trading activity and value.
The circulating supply is a crucial metric for assessing a cryptocurrency’s market capitalization. It’s beneficial when comparing cryptocurrency tokens with different issuance models or strategies, as it offers a more straightforward way to analyze the relative size and value of other cryptocurrencies.
How to Calculate the Circulating Supply?
You might find multiple options online regarding the best formula for calculating the circulating supply. The most popular formula might be:
Circulating Supply = Market Capitalization/Price
However, this formula might not always help you if you think about it. Why? To calculate the market cap, you must first know the circulating supply, right? Otherwise, how can you use the formula “Market capitalization = Price * Circulating supply”?
Therefore, this formula may be helpful when you need to check the circulating supply; however, calculating it in this manner can be challenging. Still, you can keep in mind that the circulating supply can be calculated by excluding other supplies from the total supply as follows:
- Take the total supply of a particular coin or token.
- Look for all the tokens held by the project’s team or developers.
- Identify all the tokens locked in smart contracts.
- Exclude tokens reserved for various purposes (e.g., ecosystem development, partnerships, future use).
- Subtract the tokens that were burned or permanently removed from circulation.
Other sources may consider different formulas, too. For instance, you might also find sources that tell you to calculate the circulating supply by taking the total supply and subtracting the tokens that were burned.
These differences in the formulas used to calculate the circulating supply may come from the fact that no one can say what the circulating supply of Bitcoin, for instance, is. All the circulating supplies you see online are approximations.
Of course, they are carefully calculated by considering all the data at hand, but it is tough to determine the exact circulating supply for a particular cryptocurrency.
Worried about token inflation?
Learn how fully diluted market cap shows the future impact of new token supply understand FDV before you invest
The Impact of the Circulating Supply in Crypto
Circulating supply affects investment decisions by influencing a cryptocurrency’s availability and perceived scarcity. Additionally, investors may consider other factors as well. So, let’s break down the most popular one.
Circulating Supply and Crypto Adoption
For cryptocurrencies seeking to gain mainstream adoption, the circulating supply plays a crucial role in accessibility.
A high circulating supply often translates to a lower price per coin, making it more affordable and potentially more appealing to a broader group of investors. This accessibility can help build a larger community, increase trading volume, and boost adoption.
How Does Circulating Supply Impact the Price of a Cryptocurrency?
Simply put, the circulating supply can highly influence the price of a coin. Generally, when the circulating supply is high compared to demand, prices tend to remain lower, as there’s ample availability for buyers.
On the other hand, when the circulating supply is low and the demand is high, scarcity can drive up the price. This supply-demand balance is crucial to the price action in cryptocurrency markets, where sudden changes in supply can lead to dramatic price falls or unexpected price rises.
Circulating Supply and Mining
For cryptocurrencies that leverage a PoW (Proof of Work) consensus mechanism, such as Bitcoin, which uses mining to confirm transactions, the circulating supply gradually increases as miners unlock new coins.
This gradual increase affects the market by introducing new coins that can be traded, which, in turn, influences supply and may impact prices. Mining is, therefore, a mechanism that directly influences both the circulating supply and the potential rewards for investors, in addition to many other concepts, such as transaction fees.
Circulating Supply and Market Capitalization
Market capitalization is often used to rank cryptocurrencies. Changes in circulating supply will directly influence market capitalization (consider the formula), affecting the size of a cryptocurrency compared to others.
For investors, the market cap is a reference to analyze a crypto asset’s position in the crypto market (and not only) and make investment comparisons to decide which assets to add to their portfolios.
Are you tracking the wrong number?
Understand how market cap and supply shape a coin’s real value read the full comparison
Circulating Supply vs. Total Supply vs. Maximum Supply
Let’s get straight to the beginning. The circulating supply differs entirely from the total and maximum supply. The differences between these three concepts can help investors understand a project’s potential for future growth and scarcity. So, let’s take them one at a time:
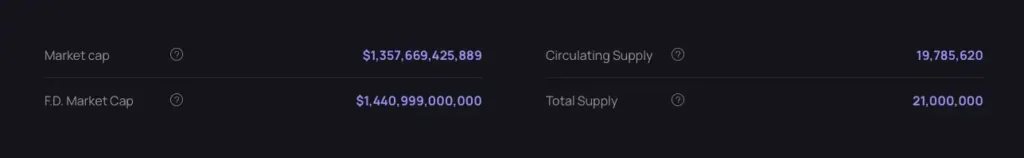
- Total Supply: This refers to the total number of coins currently in existence, excluding those that have been burned or removed from circulation, but including those held in reserve. It represents the overall supply but does not reflect the immediate availability of coins for trading. For example, at the time of writing, Bitcoin’s total supply is 19.78 million.
- Maximum Supply: This is the maximum number of coins that will ever exist for a specific cryptocurrency. For example, Bitcoin has a limited supply of 21 million coins. Once this limit is reached, no new coins will be mined or introduced, which can significantly impact the coin’s value over time as scarcity increases.
Sidenote: Remember that some digital assets do not have a maximum supply. For example, Ethereum doesn’t have a maximum supply; instead, it operates based on a burning mechanism to maintain scarcity for its tokens.
The Relationship Between the Supplies
When new tokens or coins are added to the circulating supply, the value per coin can decrease due to increased availability.
On the other hand, removing coins from the circulating supply through burning or staking, for example, can increase value due to scarcity. This dynamic between circulating and maximum supply creates an ongoing balance in price, investor interest, market cap, and the overall market value.
Is volume the real market signal?
Learn how trading volume reveals buyer strength and short term momentum see how volume really works
FAQ
Yes, burning removes coins from circulation, reducing the circulating supply, which can create scarcity and potentially raise prices.
It depends on the project’s goals. A high circulating supply can make the coin affordable, increasing accessibility, but it may also limit price growth due to greater availability.
When the circulating supply of a cryptocurrency reaches its limit, no new coins will be introduced, potentially increasing the value if demand persists as scarcity increases.
Yes, the circulating supply can decrease when talking about token-burning events.
Final Thoughts
Leveraging the circulating supply is usually extremely helpful, especially when analyzing a project’s market potential, scarcity, and value. This metric, along with others such as total and maximum supplies, and market capitalization, provides insights into a coin’s availability, potential growth, and supply-demand dynamics.